One disease alone accounts for 20 per cent of global deaths.
Bacterial infections, caused by harmful bacteria growing inside the body, show up in many forms. There are skin infections, respiratory tract infections, the dreaded “gastro” or food poisoning, sexually transmitted diseases and urinary tract infections.
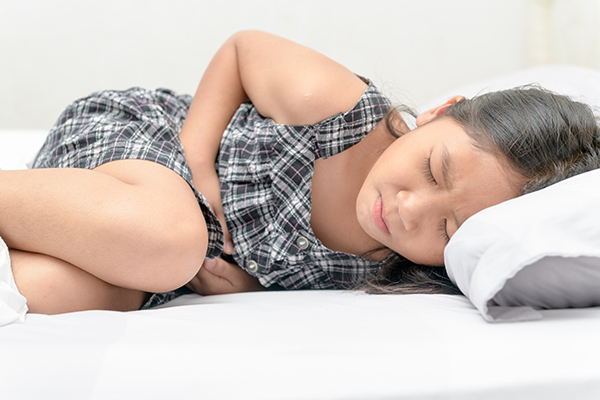
Sepsis
One in five people worldwide die of sepsis, which occurs when bacteria enter the blood and rapidly grow, triggering an inflammatory response cascade that causes septic shock, organ failure, and, if not treated quickly enough, death. In 40 per cent of cases, the type of bacteria causing the infection isn’t identified in time, making it difficult to treat and causing the cascade of bodily responses that can become fatal.
Pneumonia
The leading cause of death in children under five worldwide, pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, cough, fever or chills and phlegm. Pneumonia caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics, and one of the most common types of pneumonia, caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, can be prevented by vaccination.
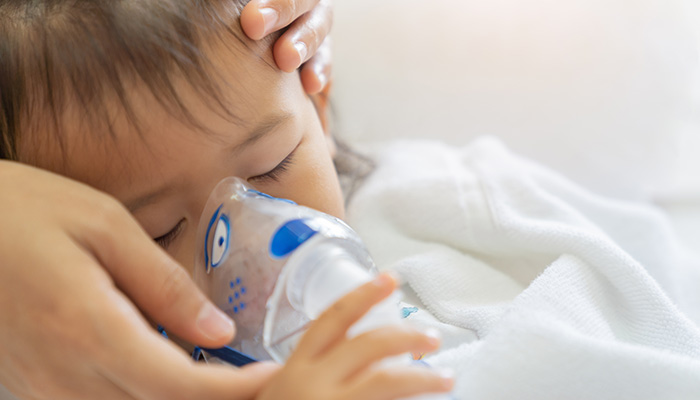

Urinary tract infections (UTI)
These infections occur when bacteria enter and multiply in any part of the urinary system, most commonly in the bladder and urethra. UTIs are mainly caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) and are the most common infection in humans worldwide. Symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, blood in the urine, and strong-smelling urine. While UTIs can usually be easily treated with antibiotics, they can cause death if they develop into sepsis. An estimated one-third of sepsis cases begin as UTIs.
Prior to the invention of antibiotics, more than half of all deaths were due to infection
BY THE NUMBERS
Prior to the invention of antibiotics,
more than half of all deaths
were due to infection.
50%
Meningitis
This infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, the meninges, causes fever, neck stiffness and pain, and a rash of purple or red spots that remain when you press on them. While this disease can be caused by a virus or a fungus, bacterial meningitis is the most severe type, and can turn fatal within hours.

Wound infections
A wound in your body, whether from surgery or injury, allows bacteria to enter the body and cause disease. An infected wound can swell, become red, feel warm, and ooze pus. Chronic wounds affect 40 million people worldwide, including 420,000 Australians, each year. The ageing population and increase in people with type 2 diabetes are drivers of an increase in chronic wounds. If bacteria infecting a wound spread through the body and into the blood, it can trigger sepsis.
Tuberculosis (TB)
TB is a lower respiratory tract infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which infects the lungs. It remains a major killer because of a rise in drug-resistant strains. The vaccine against TB is one of the most widely used worldwide.
Diarrhoea
Diarrhoea is the second-leading cause of death in children under five worldwide, killing over half-a-million children of this age globally each year. Previously, most deaths from diarrhoea were caused by the accompanying dehydration, but sepsis resulting from bacterial infection represents a growing proportion. Diarrhoea is a symptom of a range of infections, including bacterial, viral and fungal. Infection with E. coli is one of the most common causes of diarrhoea.

