Outer space has long been a source of fascination and exploration but if you’re serious about discovering new life forms, swap telescopes for microscopes and shift your gaze downwards instead.
On the surface, soil may appear lifeless but dig a little deeper and you’ll discover it’s teeming with microbial life, invisible to the naked eye. Each gram of soil contains about 1000 different species of bacteria, some of which produce chemical compounds that are the source of modern medicine.
In fact, more than half of the world’s currently prescribed antibiotics come from natural sources – such as soil – and more than 60 per cent of anticancer drugs.
Here are 10 common medications derived from nature:
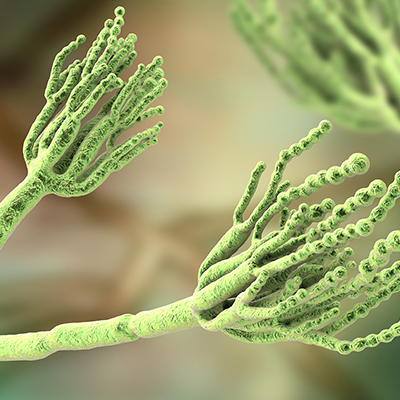 Penicillin
Penicillin
British microbiologist Alexander Fleming discovered Penicillin, the world’s first antibiotic, from the Penicillium notatum mould in 1928. This ground-breaking drug is still used to treat bacterial infections caused by strains of staphylococci and streptococci such as pneumonia, meningitis and septicaemia. It can also be used to treat anthrax, botulism and tetanus.
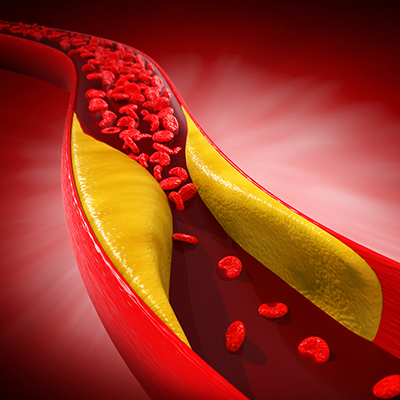 Statins
Statins
Statins are a class of lipid-lowering medications, commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol levels, and were developed from molecules produced by fungus. These molecules were discovered in various fungi by biochemists and scientists across Japan, UK and US in the 1970s and 1980s. Statins are also used as a primary preventative treatment in people at risk of developing cardiovascular disease as well as a secondary treatment to lower the mortality rate in those who have cardiovascular disease.
 Aspirin
Aspirin
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), known by the brand name Aspirin, was inspired by the use of salicylic acid, derived from the bark and leaves of willow trees to treat fever, pain and inflammation throughout history. In 1853, chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt treated sodium salicylate with acetyl chloride to produce ASA for the first time and scientists worldwide refined his formula to develop Aspirin by 1899. As well as reducing pain, fever and inflammation, it is used to treat Kawasaki disease, pericarditis and rheumatic fever and to prevent heart attacks, ischaemic strokes and blood clots.
 Avermectins
Avermectins
Avermectins are a series of drugs and pesticides used to treat parasitic worms, such as those that cause river blindness, and insect pests. They are derived from Streptomyces avermitilis, an actinomycete discovered in 1978 from a soil sample collected at Itō in Japan’s Shizuoka Prefecture. Biologist and parasitologist William C. Campbell and biochemist Satoshi Ōmura were awarded the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their roles in discovering avermectins, which were first developed as a veterinary medication.
 Rifampicin
Rifampicin
Rifampicin is an antibiotic developed in 1965 from the soil bacterium Amycolatopsis rifamycinica which was discovered in a soil sample taken from a pine forest on the French Riviera. It is used to treat several types of bacterial infection including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, leprosy and Legionnaires’ disease.
 Capreomycin
Capreomycin
An anti-inflammatory antibiotic, Capreomycin was discovered in the United States in 1960 and developed from the soil bacterium, Streptomyces capreolus. It is used in combination with other antibiotics to treat tuberculosis and is prescribed as a second-line treatment for active drug-resistant tuberculosis.
 Vancomycin
Vancomycin
A soil sample collected from the interior jungles of Borneo by missionary Rev. William M. Bouw yielded the Amycolatopsis orientalis organism which led to the development of Vancomycin in 1953. This antibiotic is used to treat bacterial skin and bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
 Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin was discovered during an organised effort in the 1950s to find anticancer compounds in soil-based microbes. A new strain of Streptomyces peucetius bacteria was found in a soil sample taken from the grounds of Castel del Monte, a 13th-century Italian castle. Sold under the brand name Adriamycin, Doxorubicin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat breast and bladder cancers, Kaposi’s sarcoma, lymphoma and acute lymphocytic leukemia.
 Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine was isolated in 1971 from Tolypocladium inflatum, a new strain of fungus discovered in soil samples from Norway. Its immunosuppressive properties were quickly discovered and Cyclosporine came into medical use in 1983 and was listed on the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) List of Essential Medicines. It is used to treat psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and nephrotic syndrome. It is also used to prevent rejection in organ transplants and in eye drops for keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eyes).
 Aureomycin
Aureomycin
Aureomycin, also known as chlortetracycline, was the first tetracycline antibiotic identified. It was discovered by plant physiologist Benjamin Minge Duggar in 1945 as the product of Streptomyces aureofaciens, a bacteria he cultured from a soil sample collected from the University of Missouri’s Sanborn Field. It is used to treat allergic dermatitis in humans as well as conjunctivitis, infected wounds and respiratory tract infections in animals.

Help us find the next antibiotic
Media: IMB Communications, +61 (7) 3346 2134, communications@imb.uq.edu.au.
